What does a data analyst do? Complete career guide for freshers

Ever wondered how Netflix knows exactly what you want to watch next or how Swiggy predicts your delivery time so accurately?
That happens through data analysis. It takes raw information and turns it into insights that help businesses make smarter decisions.
The demand for this skill is growing quickly. According to IBEF, India’s data analytics industry is projected to create over 11 million jobs by 2026, reflecting the rapid growth of analytics-driven roles. This makes analytics one of the most promising career paths for students and freshers today.
You do not need a computer science degree to begin. Curiosity, problem solving, and a willingness to work with data are enough to get started.
Table of Contents
1. What Does a Data Analyst Do?2. Key Responsibilities of a Data Analyst
3. Types of Data Analysts
4. Skills Required to Become a Data Analyst
5. Data analyst tools you must learn
6. Real-World Projects for Data Analyst Freshers
7. Best Certifications for Data Analyst Freshers
8. Average Data Analyst Salary in India
9. Growth Path in a Data Analytics Career
10. Conclusion: Ready to Begin Your Journey?
11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What does a data analyst do?
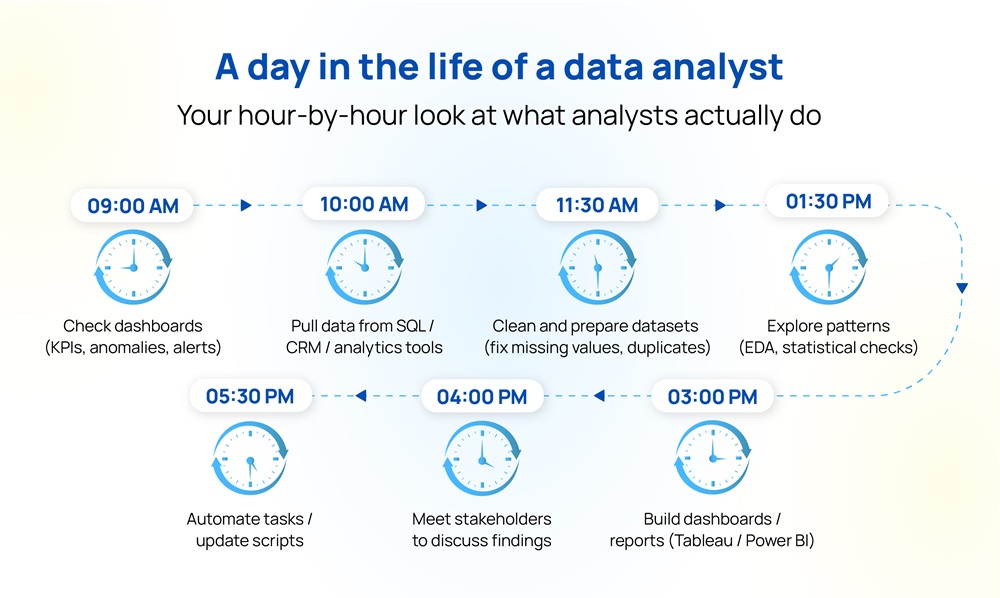
A data analyst helps organisations make decisions based on evidence, not assumptions. Every business collects data, but it becomes valuable only when someone can interpret it, find what matters, and translate it into actions.
For freshers entering the field, data analyst jobs typically include three major areas:
1. Understanding the problem
Analysts work with business, product or marketing teams to understand what needs to be solved. It could be declining user engagement, inconsistent sales, rising operational costs or the performance of a new campaign. Before touching data, analysts clarify the question they need to answer.
2. Working with data
This involves data collection using SQL, cleaning it, exploring patterns, running analyses in Excel or Python and building dashboards that show the story clearly. Freshers often start with smaller analytical tasks that build their confidence and technical depth.
3. Communicating insights
A big part of the job is explaining what the data reveals and why it matters. Analysts convert findings into recommendations teams can act on. Even early in your data analysis career, the insights you share can influence product updates, marketing strategy, pricing decisions, and operational improvements.
🔍 What kinds of questions do analysts help companies answer?
- What is causing customer drop-offs in the app?
- Which channels bring the highest quality leads?
- How can we forecast demand more accurately?
- Which cities or products drive the most revenue?
- What operational bottlenecks increase delivery time?
A career as a data analyst blends technical skills with business understanding, which is why they are valued across industries. As a fresher, you get exposure to decision-making, cross-functional collaboration, and real business challenges early in your career.
Now that you know the role at a high level, here is what data analysts actually work on day-to-day.
Key responsibilities of a data analyst
A data analyst’s responsibilities far beyond running reports or making dashboards. Companies rely on analysts to understand what is happening in the business, identify patterns, and support decisions with data instead of assumptions. For freshers, these are the key responsibilities that are a part of a data analysts job description:
1. Collecting and organising data
Analysts pull raw data from different sources such as databases, spreadsheets, CRM tools, marketing platforms, and product analytics data systems. The first step is always understanding where the data lives and ensuring it is accurate.
2. Cleaning and preparing datasets
Raw data is rarely perfect. It might have missing values, duplicates, or inconsistencies. Analysts clean, structure, and prepare the data so that the results are reliable. This is one of the most important skills for freshers because good analysis starts with good data.
3. Exploring and analysing patterns
Once the dataset is ready, analysts study trends, compare performance across time periods, run basic statistical checks, and try to understand what the numbers are revealing. This is where curiosity and problem-solving matter.
4. Creating dashboards and reports
Teams depend on dashboards to monitor performance every day. Analysts use tools like Excel, Power BI, Tableau, or Looker to create clear visuals that show KPIs, trends, and insights in a way non-technical teams can understand.
5. Presenting findings to stakeholders
Insights only matter when people understand them. Analysts explain what the data says, why it matters, and what actions the team should consider. Freshers often present insights to product managers, marketers, operations teams, or leadership.
6. Answering ad-hoc business questions
Companies constantly have new questions. Why did a metric drop? Which campaign is underperforming? Where are users dropping off? Analysts are the first people teams turn to when they need answers quickly.
7. Automating recurring tasks
As you grow, you will use programming languages to write scripts in SQL or Python to automate reports, reduce manual work and improve efficiency. This is one of the ways analysts add long-term value to the organisation.
8. Supporting experiments and decisions
Analysts often help validate hypotheses, run A/B tests and measure the impact of new features or campaigns. Even as a fresher, you will be part of decisions that shape product strategy or business growth.
These responsibilities exist across industries, but the exact nature of your work depends on the kind of analyst role you choose.
Types of data analysts
Data analytics roles vary based on the kinds of decisions a company needs to make. Here are the most common types of analysts freshers can explore:
Business data analyst
Works on revenue trends, customer behaviour and overall business performance. They support leadership teams with insights that guide strategy, planning, and forecasting.
Marketing data analyst
Marketing data analysts gather data, campaign performance, audience insights, website analytics, conversions, and lead quality. This role is common in digital-first companies, agencies and startups.
Product data analyst
Studies how users interact with a product. They analyse user journeys, drop-offs, feature usage, and A/B tests to help product teams build better experiences.
Financial data analyst
Works with budgets, pricing, forecasts, risk analysis, and financial models. These analysts are valued in banks, fintech, corporate finance, and investment teams.
Operations data analyst
Improves internal processes across logistics, supply chain, delivery operations, and workforce planning. This role is important in manufacturing, retail, e-commerce, and service companies.
Healthcare data analyst
Uses patient records, hospital data, and treatment outcomes to support clinical decisions, policy-making, and quality improvement.
Research data analyst
Works in academic institutions, think tanks, or government initiatives to interpret large datasets for research and policy insights.
Whichever path you choose, you will need a strong foundation in certain technical and soft skills.
Skills required to become a data analyst
If you are just starting out, think of these skills as your data analyst roadmap — a clear path that helps freshers learn the right concepts in the right order
Technical skills
From programming languages to tools, here are some important tools that will help you interpret data in your job.
Excel: Still the starting point for most analytics work. Freshers use Microsoft Excel for data entry, formulas, pivot tables, charts, data cleaning, and quick data analysis.
SQL: The most important skill for analysts. SQL helps you extract data from databases, join tables, filter information, and prepare datasets for deeper data analysis.
Python or R: Python is beginner-friendly and widely used for automation, analysis, and visualisation. Freshers who know Python stand out in interviews.
Statistics fundamentals: Concepts like averages, variance, probability, correlation, and hypothesis testing help you understand whether insights are meaningful.
Data cleaning: Handling missing values, removing duplicates, and fixing inconsistencies is a core part of the job. Employers value candidates who understand this early.
Data visualisation: Tools like Tableau or Power BI help you present insights clearly. Freshers often start with basic dashboards and grow from there.
Business understanding: Even technical roles need context. Knowing what a company cares about (revenue, users, retention, cost, conversions) improves your analysis.
Now that we have explored the technical skills, let’s take a look at crucial soft skills of a successful data analyst.
Soft skills
Problem solving: The ability to break a question into smaller parts and approach it logically.
Communication: Analysts explain insights to non-technical teams. Clear communication matters as much as technical accuracy.
Curiosity: Good analysts ask “why” until they reach the root cause of a trend.
Attention to detail: Small errors in cleaning or calculations can change the outcome.
Collaboration: Analysts work with product managers, marketers, engineers, and finance teams, so teamwork is essential.
Once you build these essential data analyst skills, the next step is learning the tools that analysts use every day.
🎓 Beginner-friendly learning order
- Excel
- SQL
- Data cleaning basics
- Python fundamentals
- Tableau or Power BI
Data analyst tools you must learn
If you are wondering how to become a data analyst, do not worry, you do not need to master every tool at once. Freshers should focus on the essentials and add more tools as they grow.
Excel: Best for quick analysis, reporting and basic dashboards. Still widely used across industries.
SQL: Almost every company expects working knowledge of SQL. You will use it every day to extract and prepare data.
Python: Useful for automation, data cleaning, statistical data analysis, and visualisations. Growing more important for entry-level roles.
Power BI: Popular in corporate and enterprise environments for building interactive dashboards.
Tableau: A visualisation tool used by many analytics, consulting and tech teams. Helps simplify complex insights.
Google Analytics / GA4: Important for marketing and product analysts who work on website or app data.
Jupyter Notebook / Google Colab: Common environments for Python-based data analysis and experimentation.
GitHub: Helps you store projects, share code and build a public portfolio that recruiters can evaluate.
These tools come to life when you start working on real datasets. Here are portfolio-friendly data management projects you can build as a fresher
Real-world projects for data analyst freshers (portfolio ready)
One of the best ways to stand out as a fresher is by building a portfolio that proves your skills. You do not need company experience to do this. You can use public datasets from Kaggle, Google, GitHub, or government portals.
Here are strong beginner-friendly project ideas:
Sales performance dashboard: Analyse sales by region, product, time period, and customer segments. Create a dashboard in Excel, Tableau or Power BI.
Customer churn analysis: Use sample telecom or subscription datasets to find why customers stop using a service. Highlight the biggest churn indicators.
Marketing campaign analysis: Study impressions, clicks, conversions, and ROI using mock or open marketing datasets. Identify top-performing channels.
E-commerce insights project: Explore product popularity, cart behaviour, order patterns, repeat purchases, or delivery time trends.
Stock market trend analysis: Use freely available stock datasets to analyse price movements and build basic forecasting models.
HR analytics dashboard: Track hiring, employee retention, performance ratings, and attrition patterns.
Movie or streaming analytics: Study IMDB or streaming datasets to find genre trends, viewer ratings, and user behaviour.
A portfolio with 3–5 such projects shows recruiters that you understand the full workflow: cleaning data, analysing it, and presenting insights clearly.
Interview prep is a big part of starting your career. To help you get started, we’ve put together a detailed list of data analyst interview questions that freshers can practise.
Best certifications for data analyst freshers (to boost your resume)
Certifications do not replace skills, but they help freshers get noticed — especially when your resume is competing with hundreds of applicants. These are some of the most recognised certifications that will help boost a data analyst resume for freshers:
Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate: Beginner-friendly, covers SQL, Excel, R, visualisation, and real case studies.
IBM Data Analyst Professional Certificate: Strong foundation in Python, SQL, Excel, and dashboarding.
Microsoft Power BI Data Analyst Certification: Ideal for roles that involve reporting and dashboard creation.
Simplilearn Data Analyst Master’s Program: Good for freshers who want structured learning across tools and concepts.
Coursera Data Analysis with Python: Quick, practical course to build confidence in Python, which is the most common among programming languages.
Udacity Business Analytics Nanodegree: Focuses on business-focused data analysis and decision-making.
Excel and SQL specialisations (Coursera / Udemy): Still two of the most important skills for entry-level analysts.
You do not need all of them. Choose 1–2 certifications that match the tools you want to specialise in to become a successful data analyst.
🏅 If you do not know where to start
Begin with the Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate. It is beginner-friendly and accepted by companies across India.
Average data analyst salary in India
The average salary of a data analyst in India depends on your skills, the tools you know, and the industry you work in. Freshers typically start in junior analyst roles, while salaries grow quickly with experience — especially if you specialise in SQL, Python, dashboards, and business data analytics.
Entry-level (0–2 years) – ₹3.5 lakh to ₹6.5 lakh per year
Early career (2–4 years) – ₹6 lakh to ₹10 lakh per year
Experienced data analyst (4–7 years) – ₹10 lakh to ₹16 lakh per year
Senior data analyst (7+ years) – ₹15 lakh to ₹25 lakh per year, depending on the sector and technical depth
Industries that offer higher salaries
- Tech and product companies
- BFSI (banking, financial services, insurance)
- Consulting
- E-commerce
- SaaS and startups
Cities like Bangalore, Hyderabad, Gurgaon, Pune, and Mumbai tend to pay at the higher end of the spectrum because of strong data analytics demand.
📘 Want BFSI GCC–specific salary benchmarks?
If you want a sector-wise breakdown of data analyst salaries across investment banking, retail & commercial banking, financial services, and insurance, you can download our detailed report here:
[Download the Careernet BFSI GCC Salary Benchmark Report]
Growth path for a career as a data analysts
Many freshers enter the field as junior analysts, but the long-term growth in a data analytics career is one of its biggest advantages. As you gain technical skills, business understanding, and experience working with larger datasets, you can move into more advanced and specialised roles. Here is what a typical career journey looks like for analysts in India.
1. Junior data analyst (0–2 years)
At the beginning of your career, most of your work revolves around cleaning present data, organising unstructured data, validation, basic reporting, dashboard building, and writing simple SQL queries. You support senior data analysts and contribute to smaller analytical tasks that help you understand business processes. This stage builds your foundation in analytical skills, data quality practices, and data processing techniques.
2. Data analyst (2–4 years)
As you gain confidence, you start taking ownership of full analysis cycles. You work with stakeholders, interpret data independently, and present data insights that influence decisions. Many analysts at this stage begin learning more advanced statistical analysis, predictive analytics, and data visualisation techniques. You also start collaborating more closely with data engineers and product teams.
3. Senior data analyst (4–7 years)
Senior analysts handle complex datasets, design experiments, optimise reporting systems, and guide junior team members. You may work on advanced analytics, diagnostic analytics, forecasting models, and business intelligence projects. This is also the stage where many analysts decide whether they want to specialise or move into leadership roles.
4. Specialisation paths
Depending on your strengths, you can explore roles such as:
- Business intelligence analyst – focuses on reporting systems, dashboards, and enterprise-wide data tools.
- Product analyst – works on product behaviour, cohort analysis, A/B tests, and growth experimentation.
- Data scientist – Data scientists focus on machine learning, predictive modelling, data mining, and advanced statistics.
- Analytics engineer – bridges the gap between analysts and data engineers by building scalable data pipelines.
- Business analyst – blends data insights with process optimisation and strategic recommendations.
5. Leadership roles
Experienced data analysts can grow into roles including Analytics Manager, Data Science Manager, Head of Analytics, or even Chief Data Officer in mature organisations. These roles involve strategic planning, building data teams, overseeing data governance, and driving data-driven decision-making across the company.
This clear progression makes analytics one of the most stable and rewarding career paths for freshers entering the workforce today.
Start your journey in data analytics with MyCareernet
For freshers who enjoy problem-solving, patterns, and understanding how things work, data analytics offers a clear, future-proof career path. Learning SQL, Excel, Python, and visualisation data tools is enough to get started, and your growth becomes faster as you work on real-world projects and gain business context. With strong demand across industries, data analytics gives you both stability and long-term career mobility.
If you are planning your next step, this is a great time to apply for jobs on MyCareernet and explore data analytics opportunities curated for early-career talent.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, data analytics is one of the most in-demand career paths for freshers because companies across every sector rely on data to make decisions, and entry-level roles have strong salary growth and learning opportunities.
Basic coding is helpful but not mandatory to start. Many freshers begin with Excel and SQL, then learn Python gradually as they advance.
Data analytics focuses on interpreting existing data to make decisions, while data science involves building predictive models, using advanced statistics, and working with machine learning.
With consistent learning, most freshers can become job-ready in 3–6 months by mastering Excel, SQL, basic Python, and 2–3 portfolio projects.
Dashboards, sales analysis, churn analysis, marketing data analytics, e-commerce insights, or any project that shows data cleaning, trend analysis, and clear presentation of insights.
Tech, BFSI, e-commerce, healthcare, consulting, manufacturing, retail, logistics, SaaS, and startups all hire data analysts at scale
Both work well, but Power BI is preferred in Indian corporates and BFSI, while Tableau is popular in tech, consulting and product-focused companies.
The scope is growing rapidly as companies adopt automation, AI and data-driven operations, creating new roles in product analytics, business data analytics, financial analytics and AI-assisted decision-making.

MyCareernet
Author
MyCareernet brings expert insights and tips to help job seekers crack interviews and grow their careers.

